Search Engine Optimization
From The Yaffe Center
(→Legal precedents) |
(→Legal precedents) |
||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
In 2002, SearchKing filed suit in an Oklahoma court against the search engine Google. SearchKing's | In 2002, SearchKing filed suit in an Oklahoma court against the search engine Google. SearchKing's | ||
claim was that Google's tactics to prevent spamdexing constituted an unfair business practice. In | claim was that Google's tactics to prevent spamdexing constituted an unfair business practice. In | ||
| - | May 2003, the court pronounced a summary judgment in Google's favor. | + | May 2003, the court pronounced a summary judgment in Google's favor.[http://news.cnet.com/2100-1032_3-1011740.html] |
In March 2006, KinderStart.com, LLC filed a First Amendment complaint against Google and also | In March 2006, KinderStart.com, LLC filed a First Amendment complaint against Google and also | ||
| - | attempted to include potential members of the class of plaintiffs in a class action.[ | + | attempted to include potential members of the class of plaintiffs in a class action.[http://www.glawinfo.com/download/KSC_Complaint_1stAmd_Filed.pdf] The plaintiff's |
web site was removed from Google's index prior to the lawsuit and the amount of traffic to the site | web site was removed from Google's index prior to the lawsuit and the amount of traffic to the site | ||
plummeted. On March 16, 2007 the United States District Court dismissed KinderStart's complaint | plummeted. On March 16, 2007 the United States District Court dismissed KinderStart's complaint | ||
Revision as of 20:41, 26 March 2011
What is Search Engine Optimization
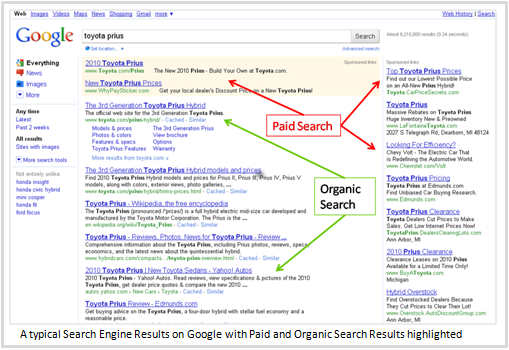
Search Engine Optimization or SEO is a marketing strategy used to improve the ranking of a web page in the organic or unpaid section of online search engines such as Google, Bing, Yahoo, Yandex, Baidu, Naver, and others. This is different from the paid search campaigns which is sometimes referred as the Search Engine Marketing.
As part of any SEO strategy webmasters uses various techniques of webpage design to improve the likelihood of that page coming on top when a person executes a search with specific keywords. Most popular search engines ranks webpages and not websites using a method called indexing to determine which webpages shows up at top for specific keywords.
As a marketer responsible for digital or online marketing it is important that your organization’s pages appear at top of search queries. It is estimated that the click through rate (CTR) for natural sections of search engines is 75% compared to 25% for the paid sections[1]. In addition, 63% of the clicks are performed on the top three search results[2]. Therefore, if an organization’s links are not appearing at the top of search results people are not going to find its products or services.
It is important to note that people often don’t make online purchase decisions by clicking on the unpaid section of search engines. Therefore, the unpaid sections have been viewed as an important area to promote the awareness of a company’s products or services. It is essential that an organization prioritizes the online metrics that it want to drive through its SEO strategies.
Other areas to improve SEO objectives are videos, images, podcasts, news, PDFs. All these different web contents need slight adjustments to improve the SEO performance.
SEO is also commonly used as an acronym for Search Engine Optimizers. These are consultants or service providers who can help their client to improve their webpage pagerank[3].
Following is the 7 largest search engines engine ratings on the global usage.[4]
1. Google 55.2%
2. Yahoo 21.7%
3. MSN Search 9.6%
4. AOL Search 3.8%
5. Terra Lycos 2.6%
6. Altavista 2.2%
7. Askjeeves 1.5%
Techniques to improve SEO
From Google’s standpoint, pagerank of a webpage is dependent on the following factors:
- The age of the domain and the relevance of its content. It is based on the premise that stable webpages are more trustworthy.
- The number of other sites linked to the webpage. When a number of websites are referring to a webpage it is taken as a vote of confidence.
Therefore, webmasters uses the following techniques to improve SEO. It is estimated that 25% of the SEO can be attributes to on-page techniques and 75% to off-page techniques.
- Keywords
- Title tags, meta data and URLs
- Content
- Internal linking (helping the spiders find your site)
- Blogs
Off-Page SEO (factors outside your site affecting ranking)
- Link-building
- Getting new Links
- Link bait
- Blogs
- Social media
Other Types of Search Engine Optimization
SEO isn’t just for regular websites and the big three search engines. There are other types to optimize web site for local and mobile search, as well as social media.
Most commonly used SEO terminologies:
- Pagerank[5]
Google optimization
The following ranking factors were rated by our panel of 72 SEO experts. Their feedback is aggregated and averaged into the percentage scores below. For each, we’ve calculated the degree to which the experts felt this factor was important for achieving high rankings as well as the degree of variance in opinion, estimated using the standard deviation of the contributors’ answers. Thus, factors that are high in importance and low in contention are those where experts agree the most that the factor is critical to rankings.
Naver optimization
Case Study: Search Engine Optimization Success Stories:
Legal precedents
In 2002, SearchKing filed suit in an Oklahoma court against the search engine Google. SearchKing's claim was that Google's tactics to prevent spamdexing constituted an unfair business practice. In May 2003, the court pronounced a summary judgment in Google's favor.[6] In March 2006, KinderStart.com, LLC filed a First Amendment complaint against Google and also attempted to include potential members of the class of plaintiffs in a class action.[7] The plaintiff's web site was removed from Google's index prior to the lawsuit and the amount of traffic to the site plummeted. On March 16, 2007 the United States District Court dismissed KinderStart's complaint without leave to amend, and partially granted Google's motion for Rule 11 sanctions against KinderStart's attorney, requiring him to pay part of Google's legal expenses.
Suggested Readings
- http://www.searchengineguide.com
- http://www.seomoz.org/
- http://www.interleado.com/blog
- http://www.seoconsultants.com
- http://adwords.blogspot.com
- http://analytics.blogspot.com
- http://analytics.blogspot.com
- http://googlewebmastercentral.blogspot.com
- http://www.bgtheory.com/blog
- http://searchengineland.com
- http://blog.searchenginewatch.com/blog
- http://cf.us.biz.yahoo.com/e/100514/live10-q.html