On-Page SEO
From The Yaffe Center
(→Keywords in Your Site’s Body Text) |
|||
| (46 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | On-Page SEO techniques are those which can be done in your site to improve the ranking of the webpages in search results. These techniques are obviously within the control of | + | On-Page SEO techniques are those which can be done in your site to improve the ranking of the webpages in search results. These techniques are obviously within the control of webmasters and relatively easier to accomplish when proper attention is given.However, it should be noted that web pages should be designed to offer superior content to the visitor rather than stuffing the page with keywords. |
| - | ===== Web site Content | + | [[Image:Metatitleurl.jpg|thumb|right|444x160px|alt=Title Tags, Meta Data and URLs displayed in search result|Google search result]] |
| + | |||
| + | ==== Web site Content ==== | ||
It is always advised to create content with your visitor in mind rather than just for search engine optimization. Mention keywords within content when it makes sense rather than stuffing the web page with keywords and highlighting those unnecessarily. Also, try to create unique content for each pages rather than having all pages having same content with just change in product name. | It is always advised to create content with your visitor in mind rather than just for search engine optimization. Mention keywords within content when it makes sense rather than stuffing the web page with keywords and highlighting those unnecessarily. Also, try to create unique content for each pages rather than having all pages having same content with just change in product name. | ||
| - | + | ==== Optimizing site's Keywords ==== | |
| + | |||
| + | ===== What Is a Keyword—and Why Is It Important? ===== | ||
| + | A keyword is a word that someone includes in a search query. A key phrase is a group of words that someone includes in a query. In other words, keywords and phrases are what people search for—and how they ultimately find your page on the web. | ||
| + | |||
| + | keywords are important because they’re what people are searching for. If site includes the keywords that people are searching for, it will show up higher in any search engine’s results than sites that don’t include those keywords; in fact, a site that doesn’t include the relevant keywords probably won’t show up in those searches at all. | ||
| + | |||
| + | How, then, does webmaster determine which keywords people are searching for? It’s a matter of learning how to think like the customer. In other words, marketer needes to get inside searchers’ heads to determine which words they’re using in their queries | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Performing Keyword Research===== | ||
| + | The art of determining which keywords to use is called [[Keyword research]], and it’s a key part of SEO. When web marketers know which keywords and phrases their target customers are likely to use, they can optimize web site for those words and phrases; if they don’t know how people’re searching, they don’t know what to optimize. | ||
| + | |||
| + | While web marketer can conduct extensive (and expensive) market research to determine how their target audience is searching, or even guess what the top searches are, there are simpler and more effective ways to get smart about this. Several companies offer keyword research tools, which are software utilities or web-based services that compile and analyze keyword search statistics from all the major search engines. Marketer can use the results from these keyword research tools to determine which are the most powerful keywords to include on site. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== How Keyword Research Tools Work===== | ||
| + | Most keyword research tools work by matching the thrust or content of website with keywords relevant to your content; they’ve already searched through hundreds of thousands of possible keywords and phrases on the most popular search engines and mapped the results to their own database. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Choosing a Keyword Research Tool===== | ||
| + | When it comes to choosing a keyword research tool, the most popular among SEO professionals is Trellian’s KeywordDiscovery (www.keyworddiscovery.com). Also popular with professionals is Wordtracker (www.wordtracker.com). Finally, WordZe (www.wordze.com) is an up-and-coming keyword research tool. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The best of these tools provide more than just raw keyword research data. They may also include features such as industry keyword tracking (the top keywords that drive traffic to sites in specific industries), spelling mistake research (common misspellings in user queries), related keywords, seasonal trends, and the like. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Keywords in Anchor Text===== | ||
| + | The text that contains the link—called the anchor text—is one of the ways the search engines determine the value of a link. The best way to increase the value of an outbound or intrasite link is to include keywords in the anchor text. This lets the searchbots know that the site you’re linking to is related to the keyword—and is thus a more relevant link. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Obviously, webmasters creates the link for the anchor text using basic HTML codes. This sort of linking is done automatically by most HTML editing or web page–creation programs, or master can code the text manually, like this: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''<a href="http://www.carnegiedeli.com">Some of the best pastrami sandwiches in New York can be found at the world-famous Carnegie Deli.</a>'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Keywords in the <TITLE> Tag===== | ||
| + | One of the most important things that a searchbot looks at to determine site's content is the site’s title—as determined by the <TITLE> tag. For this reason, master should include the most important keyword or phrase as site’s title—but in an organic fashion. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example, if web site is about various types of fruit, and top three keywords are apples, oranges, and peaches, you want to try to get all three of these keywords into the title. Assuming that the name of your site is The Fruit Site, here’s one way to do so: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''<TITLE>The Fruit Site: All About Apples, Oranges, and Peaches</TITLE>'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | See how this little trick works? You essentially create a title (the official name of your site) and a subtitle (after the colon), with the subtitle being used to hold the descriptive keywords. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Alternately, you may want to rename web site to include one or more relevant keywords. But this option is good only as long as the keyword stays relevant; since the keywords users search for can change over time, marketer wants to make sure web site name doesn’t become outmoded, at least in SEO terms. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Keywords in <META> Tags===== | ||
| + | Suffice it to say that <META> tags can be used to force-feed keyword information to searchbots; these are tags that only search engine crawlers see, not site’s visitors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example, the <META> KEYWORDS tag provides searchbots with the keywords master chooses to highlight on the site. Continuing the fruit example, if keywords are apples, oranges, and peaches, master might enter a <META> tag like this one: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''<META NAME="keywords" CONTENT="apples, oranges, peaches">'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that this tag works by defining the NAME attribute as keywords, and then by defining the content of the attribute as three keywords—listed one after another, separated by commas. A searchbot will read this tag, register the keywords, and—perhaps—use those keywords to help index the page. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Using Keywords in Heading Tags===== | ||
| + | More important than <META> tags are those tags used to create headings within your page’s body text. That’s because most searchbots assume (rightly so, in most instances) that a topic given its own major heading is an important topic on the site. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Many search experts now believe that lower-level tags [[Image:h2.jpg]] through [[Image:h6.jpg]] have slightly more influence on search rankings than the first-level [[Image:h1.jpg]] tag. This argues for the creation of a hierarchical heading structure on the page. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For that reason, you want to break up your copy into two or more major sections, announce each section with a heading or subheading, and include one or more keywords in each heading. When coding in HTML, headings are created using tags [[Image:h1.jpg]] through [[Image:h6.jpg]], with [[Image:h1.jpg]] being the highest-level heading and [[Image:h6.jpg]] being the lowest level. You might create a first-level heading with code like this: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:h1.jpg]]The Truth About Apples[[Image:h1_.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Keywords in Other Tags===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Keywords can also be used in other HTML tags for positive effect. For example, surrounding keywords with bold [[Image:b.jpg]], emphasized [[Image:em.jpg]], or strong [[Image:strong.jpg]] tells searchbots that this particular word or phrase is important and, thus, more relevant—and, since searchbots are all about relevancy, this is a good thing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | You should also use keywords, when appropriate, in the <IMG> tag’s ALT attribute. This attribute provides alternate text in case an image can’t be displayed, and is used to describe the image to searchbots, which can’t otherwise determine the content of an image. For example, a picture of an apple might utilize the following <IMG> ALT tag: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''<IMG SRC="apple.jpg" ALT="picture of an apple">'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Keywords in Your Site’s Body Text ===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The more often you use a keyword in your body text, the more likely it is that search system will register the keyword—to a point. If you include a keyword too many times, search system will think you’re artificially “stuffing” the keyword into your phrase, with no regard for the actual content. If you’re suspected of keyword stuffing in this fashion, don’t be surprised to see your search ranking actually decrease—or your page disappear completely from that search engine’s search results. (Search engines don’t like keyword stuffing) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Thus, you need to determine the correct [[keyword density]] when you’re optimizing the content of a web page. Many SEO experts consider an optimal keyword density to more than that could be considered search spam. If you have a lot of different keywords on a long page, you could have a density of 20 percent or more and still rank fine. If you have only a handful of keywords on a short page, a 5 percent keyword density might be too much. The key is to make sure your page is readable; if it sounds stilted or awkward due to unnecessary keyword repetition, chances are, a searchbot will also think that you’re overusing your keywords. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Moreover, It is also important to have keyword-Oriented Copywriting for the Web. That is SEO Copywriting. | ||
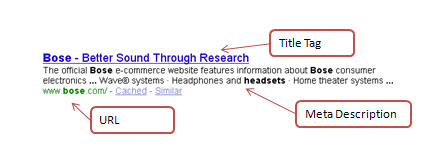
| - | + | ==== Title Tags, Meta Data and URLs ==== | |
A well optimized webpage will have a unique title and meta data. The title and meta data should be consistent with the content of the page. Also, one should write titles and meta data with keywords targeted for users. The URL of a page should have the main keyword relevant for that page …com/bluewidgets. | A well optimized webpage will have a unique title and meta data. The title and meta data should be consistent with the content of the page. Also, one should write titles and meta data with keywords targeted for users. The URL of a page should have the main keyword relevant for that page …com/bluewidgets. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 91: | ||
| - | + | ==== Internal Linking ==== | |
Internal links are a useful tool especially for large organizations as Google ranks pages based on how many other pages are linked to it. Referring and linking pages can create a ‘spider web’ of relevantly linked pages on your site. For example, Wikipedia pages are so popular in search engines because every page is linked. Google provides a useful mechanism to find pages which are relevant for a specific keyword. Conduct a Google search for: site:www.DOMAIN.com “keyword phrase.” You can now edit the pages and link the targeted word to the page that is optimized for it. Another link optimization technique is to create sitemaps to help search engine spiders find the contents. For example, Linkedin.com has an alphabetical site map to help search engines to index their pages. | Internal links are a useful tool especially for large organizations as Google ranks pages based on how many other pages are linked to it. Referring and linking pages can create a ‘spider web’ of relevantly linked pages on your site. For example, Wikipedia pages are so popular in search engines because every page is linked. Google provides a useful mechanism to find pages which are relevant for a specific keyword. Conduct a Google search for: site:www.DOMAIN.com “keyword phrase.” You can now edit the pages and link the targeted word to the page that is optimized for it. Another link optimization technique is to create sitemaps to help search engine spiders find the contents. For example, Linkedin.com has an alphabetical site map to help search engines to index their pages. | ||
| - | + | ====Blogs ==== | |
Many companies create [[blogs]] in their webpage to improve SEO. [[Blogs]] are a valuable way to attract and keep visitors interested with up to date contents. Some of the best practices are to have the blog in the domain URL e.g: com/blog. The layout should be similar to the domain site, with unique title tags, meta data, URLs and internal links. | Many companies create [[blogs]] in their webpage to improve SEO. [[Blogs]] are a valuable way to attract and keep visitors interested with up to date contents. Some of the best practices are to have the blog in the domain URL e.g: com/blog. The layout should be similar to the domain site, with unique title tags, meta data, URLs and internal links. | ||
| - | + | ==== Suggested Readings ==== | |
http://searchengineland.com/36-seo-myths-that-wont-die-but-need-to-40076 | http://searchengineland.com/36-seo-myths-that-wont-die-but-need-to-40076 | ||
Current revision
On-Page SEO techniques are those which can be done in your site to improve the ranking of the webpages in search results. These techniques are obviously within the control of webmasters and relatively easier to accomplish when proper attention is given.However, it should be noted that web pages should be designed to offer superior content to the visitor rather than stuffing the page with keywords.
[edit] Web site Content
It is always advised to create content with your visitor in mind rather than just for search engine optimization. Mention keywords within content when it makes sense rather than stuffing the web page with keywords and highlighting those unnecessarily. Also, try to create unique content for each pages rather than having all pages having same content with just change in product name.
[edit] Optimizing site's Keywords
[edit] What Is a Keyword—and Why Is It Important?
A keyword is a word that someone includes in a search query. A key phrase is a group of words that someone includes in a query. In other words, keywords and phrases are what people search for—and how they ultimately find your page on the web.
keywords are important because they’re what people are searching for. If site includes the keywords that people are searching for, it will show up higher in any search engine’s results than sites that don’t include those keywords; in fact, a site that doesn’t include the relevant keywords probably won’t show up in those searches at all.
How, then, does webmaster determine which keywords people are searching for? It’s a matter of learning how to think like the customer. In other words, marketer needes to get inside searchers’ heads to determine which words they’re using in their queries
[edit] Performing Keyword Research
The art of determining which keywords to use is called Keyword research, and it’s a key part of SEO. When web marketers know which keywords and phrases their target customers are likely to use, they can optimize web site for those words and phrases; if they don’t know how people’re searching, they don’t know what to optimize.
While web marketer can conduct extensive (and expensive) market research to determine how their target audience is searching, or even guess what the top searches are, there are simpler and more effective ways to get smart about this. Several companies offer keyword research tools, which are software utilities or web-based services that compile and analyze keyword search statistics from all the major search engines. Marketer can use the results from these keyword research tools to determine which are the most powerful keywords to include on site.
[edit] How Keyword Research Tools Work
Most keyword research tools work by matching the thrust or content of website with keywords relevant to your content; they’ve already searched through hundreds of thousands of possible keywords and phrases on the most popular search engines and mapped the results to their own database.
[edit] Choosing a Keyword Research Tool
When it comes to choosing a keyword research tool, the most popular among SEO professionals is Trellian’s KeywordDiscovery (www.keyworddiscovery.com). Also popular with professionals is Wordtracker (www.wordtracker.com). Finally, WordZe (www.wordze.com) is an up-and-coming keyword research tool.
The best of these tools provide more than just raw keyword research data. They may also include features such as industry keyword tracking (the top keywords that drive traffic to sites in specific industries), spelling mistake research (common misspellings in user queries), related keywords, seasonal trends, and the like.
[edit] Keywords in Anchor Text
The text that contains the link—called the anchor text—is one of the ways the search engines determine the value of a link. The best way to increase the value of an outbound or intrasite link is to include keywords in the anchor text. This lets the searchbots know that the site you’re linking to is related to the keyword—and is thus a more relevant link.
Obviously, webmasters creates the link for the anchor text using basic HTML codes. This sort of linking is done automatically by most HTML editing or web page–creation programs, or master can code the text manually, like this:
<a href="http://www.carnegiedeli.com">Some of the best pastrami sandwiches in New York can be found at the world-famous Carnegie Deli.</a>
[edit] Keywords in the <TITLE> Tag
One of the most important things that a searchbot looks at to determine site's content is the site’s title—as determined by the <TITLE> tag. For this reason, master should include the most important keyword or phrase as site’s title—but in an organic fashion.
For example, if web site is about various types of fruit, and top three keywords are apples, oranges, and peaches, you want to try to get all three of these keywords into the title. Assuming that the name of your site is The Fruit Site, here’s one way to do so:
<TITLE>The Fruit Site: All About Apples, Oranges, and Peaches</TITLE>
See how this little trick works? You essentially create a title (the official name of your site) and a subtitle (after the colon), with the subtitle being used to hold the descriptive keywords.
Alternately, you may want to rename web site to include one or more relevant keywords. But this option is good only as long as the keyword stays relevant; since the keywords users search for can change over time, marketer wants to make sure web site name doesn’t become outmoded, at least in SEO terms.
[edit] Keywords in <META> Tags
Suffice it to say that <META> tags can be used to force-feed keyword information to searchbots; these are tags that only search engine crawlers see, not site’s visitors.
For example, the <META> KEYWORDS tag provides searchbots with the keywords master chooses to highlight on the site. Continuing the fruit example, if keywords are apples, oranges, and peaches, master might enter a <META> tag like this one:
<META NAME="keywords" CONTENT="apples, oranges, peaches">
Note that this tag works by defining the NAME attribute as keywords, and then by defining the content of the attribute as three keywords—listed one after another, separated by commas. A searchbot will read this tag, register the keywords, and—perhaps—use those keywords to help index the page.
[edit] Using Keywords in Heading Tags
More important than <META> tags are those tags used to create headings within your page’s body text. That’s because most searchbots assume (rightly so, in most instances) that a topic given its own major heading is an important topic on the site.
Many search experts now believe that lower-level tags ![]() through
through ![]() have slightly more influence on search rankings than the first-level
have slightly more influence on search rankings than the first-level ![]() tag. This argues for the creation of a hierarchical heading structure on the page.
tag. This argues for the creation of a hierarchical heading structure on the page.
For that reason, you want to break up your copy into two or more major sections, announce each section with a heading or subheading, and include one or more keywords in each heading. When coding in HTML, headings are created using tags ![]() through
through ![]() , with
, with ![]() being the highest-level heading and
being the highest-level heading and ![]() being the lowest level. You might create a first-level heading with code like this:
being the lowest level. You might create a first-level heading with code like this:
[edit] Keywords in Other Tags
Keywords can also be used in other HTML tags for positive effect. For example, surrounding keywords with bold ![]() , emphasized
, emphasized ![]() , or strong
, or strong ![]() tells searchbots that this particular word or phrase is important and, thus, more relevant—and, since searchbots are all about relevancy, this is a good thing.
tells searchbots that this particular word or phrase is important and, thus, more relevant—and, since searchbots are all about relevancy, this is a good thing.
You should also use keywords, when appropriate, in the <IMG> tag’s ALT attribute. This attribute provides alternate text in case an image can’t be displayed, and is used to describe the image to searchbots, which can’t otherwise determine the content of an image. For example, a picture of an apple might utilize the following <IMG> ALT tag:
<IMG SRC="apple.jpg" ALT="picture of an apple">
[edit] Keywords in Your Site’s Body Text
The more often you use a keyword in your body text, the more likely it is that search system will register the keyword—to a point. If you include a keyword too many times, search system will think you’re artificially “stuffing” the keyword into your phrase, with no regard for the actual content. If you’re suspected of keyword stuffing in this fashion, don’t be surprised to see your search ranking actually decrease—or your page disappear completely from that search engine’s search results. (Search engines don’t like keyword stuffing)
Thus, you need to determine the correct keyword density when you’re optimizing the content of a web page. Many SEO experts consider an optimal keyword density to more than that could be considered search spam. If you have a lot of different keywords on a long page, you could have a density of 20 percent or more and still rank fine. If you have only a handful of keywords on a short page, a 5 percent keyword density might be too much. The key is to make sure your page is readable; if it sounds stilted or awkward due to unnecessary keyword repetition, chances are, a searchbot will also think that you’re overusing your keywords.
Moreover, It is also important to have keyword-Oriented Copywriting for the Web. That is SEO Copywriting.
[edit] Title Tags, Meta Data and URLs
A well optimized webpage will have a unique title and meta data. The title and meta data should be consistent with the content of the page. Also, one should write titles and meta data with keywords targeted for users. The URL of a page should have the main keyword relevant for that page …com/bluewidgets.
In some cases long URL with special characters are created when they are generated via a database. In such cases it is recommended to use some third party software to generate search engine friendly static URLs.
It is important to have title tags short and to the point. Don’t try to stuff them with keywords, best practice is to keep them to about 8-9 words. In addition, it is essential to have your product or brand name appear on the title tag. SEO
[edit] Internal Linking
Internal links are a useful tool especially for large organizations as Google ranks pages based on how many other pages are linked to it. Referring and linking pages can create a ‘spider web’ of relevantly linked pages on your site. For example, Wikipedia pages are so popular in search engines because every page is linked. Google provides a useful mechanism to find pages which are relevant for a specific keyword. Conduct a Google search for: site:www.DOMAIN.com “keyword phrase.” You can now edit the pages and link the targeted word to the page that is optimized for it. Another link optimization technique is to create sitemaps to help search engine spiders find the contents. For example, Linkedin.com has an alphabetical site map to help search engines to index their pages.
[edit] Blogs
Many companies create blogs in their webpage to improve SEO. Blogs are a valuable way to attract and keep visitors interested with up to date contents. Some of the best practices are to have the blog in the domain URL e.g: com/blog. The layout should be similar to the domain site, with unique title tags, meta data, URLs and internal links.
[edit] Suggested Readings
http://searchengineland.com/36-seo-myths-that-wont-die-but-need-to-40076