Digital Literacy
From DigitalRhetoricCollaborative
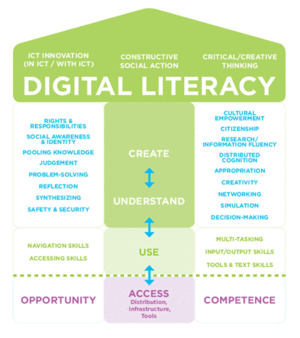
According to the National Council of Teachers of English, Digital literacy encompasses many skills used to comprehend and utilize knowledge and information gathered from digital sources or technology itself. These skills are defined by the NCTE as:
- Develop proficiency and fluency with the tools of technology;
- Build intentional cross-cultural connections and relationships with others so to pose and solve problems collaboratively and strengthen independent thought;
- Design and share information for global communities to meet a variety of purposes;
- Manage, analyze, and synthesize multiple streams of simultaneous information;
- Create, critique, analyze, and evaluate multimedia texts;
- Attend to the ethical responsibilities required by these complex environments.[1]
Literacy has evolved with technology as there is now a need for students of English to work with technology and treat it as another medium for their work. Now people must be able to interpret media, create multimodal texts through the use of digital skills, manage data, and have a certain mastery of technology related to their needs.[2].
Contents |
Digital Literacy Concepts
The traditional definition of literacy is "the ability to read and write" or "knowledge that relates to a specific subject".[3] Literacy is the first stage in a long route to mastery. Digital literacy encompasses many sub-literacies, including computer literacy, social media literacy, and many others. While having some skills in these areas is necessary, Digital Literacy in terms of writing is not simply understanding how to use a computer. Digital literacy for writing requires more thought in the philosophical, political, and cultural aspects of digital technology.
Key Frameworks
In his 2004 book Experiments in Digital Literacy, Yoram Eshet-Alkalai[4]developed a digital literacy framework that specifies five skills:
- Photo-visual skills
- Reproduction skills
- Branching skill
- Information skills
- Socio-emotional skills
Another definition comes from Wan Ng. In a 2012 article[5]Ng lays out a digital literacy framework that draws together all of these definitions and groups them into three dimensions:
- Technical
- Cognitive
- Social-emotional
Use in Education
Today students are wired to learn digitally and are immersed in the digital world with technology always within reach. Schools on all educational levels are continuously updating their curriculum to adopt and promote digital literacy in order to keep up with accelerating technological developments. This often includes the use of computers in the classroom, the use of educational software to teach the curriculum, and the course materials being made available to students online. The concept of eLearning has become popular due to the of convenience, allowing learning to take place at a time and location that’s better suited to the learner’s needs[7]. In order to effectively utilize the tools associated with eLearning, there must be a corresponding level of digital literacy.
What does all of this mean for teaching? According to the National Council of English Teacher's, the integration of multiple modes of communication provides a deeper connection to the material, and a better overall understanding of what is being taught. Multimodal literacy is a skill children acquire effortlessly. An over-emphasis on testing can deprive children of these multimodal experiences they need[8] . The integration of technology and the classroom is the simplest way to provide children with these multimodal experiences. This is because computers support software that allows nearly unlimited creative outlets for students, as well as the internet's ability to provide information instantaneously.
There is a downside to this, but it is one that is easy to combat. Children are better at learning certain things than adults,[9] including in most cases technology. Because of this, it is more important than ever for the teachers to be at least somewhat as digitally literate as the students. According to the NCTE, students who feel as though they know more than their teachers are more likely to find school irrelevant or boring[10]. Due to these factors, teachers should be prepared to devise ways to include those students that are more technologically advanced than most.
Digital Writing
Rather than digital writing being referred to as using a word processor to type text, it is thought of as how technology forces writing to evolve. Technology has provided writers with new environments and mediums to write in, and the results can reach new audiences and evoke new meanings. With more technology being created daily, it "fundamentally changes how writing is produced, delivered, and received." [11] To be able to fully understand writing, it is thought by many that teaching how to write digitally in schools should be widespread. The goal is to teach students applications for writing aside from academic papers, whether it be a blog, website, or other multimodal text.
Fair Use In Education
Educators and learners in media literacy often make use of copyrighted materials including audiovisual and digital material to convey facts and information in the classroom. Such uses, especially when they occur within a restricted-access network, do enjoy certain copyright advantages. As a practical matter, they may be less likely to be challenged by rights holders. More important, however, if challenged they would be more likely to receive special consideration under the fair use doctrine – because they occur within an educational setting.
<pThis means that educators who want to claim the benefits of fair use have a rare opportunity to be open and public about asserting the appropriateness of their practices and the justifications for them. [12] </p>
Components of Digital Literacy in the Workplace
Workplace digital literacy
Digital literacy has evolved into much more than just the ability to handle a computer - it encompasses a set of basic skills that are necessary in the production and use of digital media, participation in social networks, sharing knowledge on digital platforms, and a range of professional computing skills. These days, Digital literacy is an expected skill demanded by employers when they first evaluate a job application. It is the building block that helps users to create, communicate, and understand materials on various digital platforms in order to participate fully with a community and society as a whole.
- Communication and Collaboration. The ability to communicate clearly is important in order to collaborate with others, and create an efficient and effective workplace. Internal communication with colleagues and external communication with clients is vital for a thriving work area.
- Cyber Security. Cyberspace is heavily open to threats such as hackers, viruses, and spyware. Understanding these risks is the first step in order to prevent your computer from these digital threats.
- The Law and Ethics. Workers now, more than ever, must protecting a company's brand, intellectual property, and confidential data by taking the appropriate steps to ensure the privacy of clients and businesses. It is vital for workers to understand what protocol best ensures the privacy of fellow employees and clients.
[13].
Digital Literacy in Society
Digital literacy is increasingly growing and educators are quickly having to re-adjust and integrate social media into teaching and learning. Websites like Emma are used to create a community, open a dialogue that encourages feedback, portfolios, and interactive notes. Even apps like Facebook and Twitter connect students with experts and has taken a root as a legitimate classroom learning and communication tool. Creating, remixing, interpreting, and reevaluating ideas and information is made easier than ever before through blogging, and other social media platforms. Textual communication is imperative in growing, keeping up, and spreading ideas and concepts, as well as communication and keeping up with trends.
Visual Literacy Advantages
1. Process and make meaning of information presented in an image.
2. Communicate our own ideas through principles of design.
3. Create our own messages that capture our visual thinking in a way that conceptualizes problems to given solutions.
[14]Information and Communications Technology (ICT)
Many organizations use different terms such as ICT (information and communication technology), educational technology, computer literacy, and others. We view these terms as synonymous with digital literacy.
• Access-knowing about and knowing how to collect and/or retrieve information.
• Manage-applying an existing organizational or classification scheme.
• Integrate-interpreting and representing information. It involves summarizing, comparing and contrasting.
• Evaluate-making judgments about the quality, relevance, usefulness, or efficiency of information.
• Create-generating information by adapting, applying, designing, inventing, or authoring information [15]
Use in Society
Digital literacy is an important topic and skill because technology is developing more rapidly than society is. Because of the unprecedented capabilities and environments that technology provides, appropriate behavior and use in these digital contexts is a work in progress and may be unknowable in certain situations due to a lack of experience. Previously concrete and well-established ideas such as copyright, academic integrity, and privacy are now difficult define or in constant flux[16]. On a cultural level, digital literacy helps people communicate and keep up with societal trends. The use of eLearning in the workplace is particularly advantageous for large organizations that have a multitude of employees working in different locations working on projects and processes that require communication and collaboration with one another[17].
References
- ↑ "The NCTE Definition of 21st Century Literacies." NCTE Comprehensive News. National Council of Teachers of English, 1 Feb. 2013. Web. 10 Nov. 2015.
- ↑ "Digital Literacy Definition and Resources." University Library of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 15 Oct. 2008. Web. http://www.library.illinois.edu/diglit/definition.html
- ↑ "Literacy." Merriam-Webster. Merriam-Webster. Web. 30 Nov. 2015.
- ↑ Eshet, Hamburger. "Experiments in Digital Literacy." (2015) Web. http://www.openu.ac.il/Personal_sites/download/eshet&Amichai2004.pdf
- ↑ Ng, Wan. "Can we teach digital natives digital literacy?" Computers and Education 59. (2012) Web.
- ↑ Mohammadyari, Soheila, and Harminder Singh. "Understanding The Effect Of E-Learning On Individual Performance: The Role Of Digital Literacy." Computers & Education 82.(2015): 11-25. Academic Search Complete. Web.
- ↑ Mohammadyari, Soheila, and Harminder Singh. "Understanding The Effect Of E-Learning On Individual Performance: The Role Of Digital Literacy." Computers & Education 82.(2015): 11-25. Academic Search Complete. Web.
- ↑ "Position Statement on Multimodal Literacies." NCTE Comprehensive News. National Council of Teachers of English, 1 Aug. 2008. Web. 10 Nov. 2015.
- ↑ Lucas, Christopher G., Sophie Bridgers, Thomas L. Griffiths, and Alison Gopnik. "When Children Are Better (or at Least More Open-minded) Learners than Adults: Developmental Differences in Learning the Forms of Causal Relationships." Cognition 131.2 (2014): 284-99. Science Direct. Web. 11 Nov. 2015.
- ↑ "Position Statement on Multimodal Literacies." NCTE Comprehensive News. National Council of Teachers of English, 1 Aug. 2008. Web. 10 Nov. 2015.
- ↑ "Why Teach Digital Writing?" K A I R O S: 10.1. The WIDE Research Center Collective. Web. 30 Nov. 2015. <http://english.ttu.edu/kairos/10.1/binder2.html?coverweb/wide/index.html>.
- ↑ "Code of Best Practices in Fair Use for Media Literacy Education." NCTE Comprehensive News. National Council of Teachers of English. Web. 30 Nov. 2015<http://www.ncte.org/positions/statements/fairusemedialiteracy>.
- ↑ Hunt, Courtney, and John T. Miller. "Assessing Digital LiteracyA Framework for Developing a General Measure." Assessing Digital Literacy-A Framework for Developing a General Measure. Association for Talent Development, 2 Mar. 2015. Web. 29 Nov. 2015.
- ↑ Guymon, David. "Using Social Media to Teach Visual Literacy in the 21st-Century Classroom." Edutopia. George Lucas Educational Foundation, 03 Mar. 2014. Web. 27 Nov. 2015.
- ↑ "Digital Transformation A Framework for ICT Literacy." (2010): n. pag. Web. 30 Nov. 2015.
- ↑ "Digital Literacy Resource - Introduction." Cornell University Digital Literacy Resource. Cornell Information Technologies, 1 Jan. 2009. Web. https://digitalliteracy.cornell.edu/welcome/dpl0000.html
- ↑ Mohammadyari, Soheila, and Harminder Singh. "Understanding The Effect Of E-Learning On Individual Performance: The Role Of Digital Literacy." Computers & Education 82.(2015): 11-25. Academic Search Complete. Web.
External Links
--Samantha Lipkin April 22, 2015
